It’s a fact: solar power can slash your electricity bills while helping combat climate change, all by harnessing free, clean energy from the sun. The technology behind it, photovoltaic (PV) solar panels, is so powerful that just 90 minutes of sunlight could generate more than enough energy to power the entire world for a full year.
But here’s a question many still ask: How do solar panels work in a residential context? Many Australians are still weighing up the facts, so if you’re uncertain about home solar installation, you’re in good company.
1. What is solar power?
The sun gives us warmth and light, but it’s also a massive nuclear reactor constantly sending out energy. Tiny photons travel nearly 150 million kilometres to Earth and deliver a powerful stream of untapped energy to the solar panels on our rooftops within minutes.
Solar power captures this energy and converts it into thermal or electrical power. As the cleanest and most abundant renewable resource available, solar energy plays a key role in Australia’s move toward sustainable living.
With some of the sunniest regions in the world, Australia offers ideal conditions for solar. Homes and businesses nationwide use solar systems to generate electricity, light up interiors, maintain a comfortable climate, and heat water for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
2. How do solar panels work for your home?
For homeowners, the benefits go far beyond just savings. Installing solar panels can increase your property’s value, especially in Australia where energy efficiency is a growing priority for buyers. Many prospective buyers view solar as a long-term investment.
If you’re thinking about resale, homes with solar sell faster and at a premium, particularly when the system is fully owned (not leased) and still under warranty. Buyers are drawn to the idea of reduced power bills and sustainable living.
Before installing, consider:
- Your roof’s size, orientation, and shading
- How long you plan to stay in the home
- Available rebates or feed-in tariffs in your state
- Whether solar battery storage fits your energy usage
3. What are solar panels made of?
Over the years, solar panel technology has come a long way, from bulky, low-efficiency modules to today’s sleek, high-performance systems. Early solar panels used basic amorphous silicon with limited output, but modern systems now feature advanced materials like monocrystalline and N-type silicon for higher efficiency.
Here’s an overview of popular solar panel technologies used in Australian households.. Sorted by material, efficiency, and investment level.
| Category | Panel Type | Material Composition | Cost Tier |
| Premium | Monocrystalline Silicon (Mono-Si) | High-purity silicon wafers (single crystal) | $$$ |
| High-end | N-Type Monocrystalline | Similar to Mono-Si, but made with N-type silicon for lower degradation | $$$$ |
| Standard | Polycrystalline Silicon (Poly-Si) | Melted fragments of silicon crystals (blue-tinted panels) | $$ |
| Budget-friendly | Thin-Film (Amorphous Silicon or CdTe) | Layers of photovoltaic material on glass/plastic substrate | $ |
| Emerging Tech | Bifacial Panels | Monocrystalline cells with glass on both sides, capturing reflected sunlight | $$$$ |
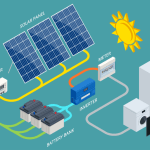
4. How do the panels create electricity?
Solar panels generate electricity through the photovoltaic (PV) effect. Each panel contains many solar cells, typically made of silicon, which is a semiconductor material. These cells are designed with two layers
- one with a positive charge (p-type)
- one with a negative charge (n-type)
When sunlight hits the panel, photons from the sun’s rays strike the silicon atoms and knock electrons loose from the atomic structure. The internal electric field within the PV cell then forces these free electrons to move toward conductive metal contacts. This flow of electrons creates direct current (DC) electricity.
The panel’s circuitry channels this DC electricity out through wires. For home use, an inverter is then required to convert the DC into alternating current (AC), which is what powers your lights, appliances, and other household devices.
Related Reading: Solar Panels Not Working? 6 Common Solar Panel Problems
5. What does the solar inverter do?
Inverters have come a long way since the 19th century. Back then, they were mechanical devices that use spinning motors to flip the direction of the electrical current. These motors switched the DC power forward and backward to mimic the flow of AC.
Today’s inverters are far more efficient. Instead of moving parts, we now use transistors, solid-state switches made from semiconductor materials like silicon or gallium arsenide.
In a solar energy system, the inverter is one of the most important components. It does this by flipping the direction of the incoming DC current, turning it into a wave-like AC output. Without this conversion, your solar energy system wouldn’t be able to power your appliances or feed electricity back into the grid.
Related reading: The Top 5 Solar Inverter Problems
Static Electrics – Your Local Experts for Solar Panel Support in Brisbane & the Sunshine Coast
Here at Static Electrics, we can advise, install, maintain, service, and even professionally clean your solar power system so that you never need to wonder or worry about how solar panels work ever again. Our local, family-owned business is fully accredited and licensed for solar repairs in Brisbane, the Sunshine Coast & beyond, so get in touch to speak to our friendly local electricians near you today.